When I first launched an ecommerce store selling human hair wigs, glueless wigs, and lace front wigs, my immediate strategy was Google Ads. Like many others, I wanted fast results.
And I got clicks—but at a very high cost.
The Turning Point: Google Ads Became Unsustainable
Google Ads gave me visibility, but the cost-per-click (CPC) in my niche was sky-high. I was spending a big chunk of my budget just to stay afloat, and the ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) wasn’t justifying it.
It didn’t take long to realize: this wasn’t scalable.
That’s when I made the pivot to Semantic SEO—and everything changed.
What Is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is about optimizing your content for meaning, not just keywords. Google is no longer just matching phrases—it’s understanding topics, context, and relationships.
Instead of targeting only “glueless wigs,” I started thinking about everything related to that term: how to use it, who needs it, what features matter, and how it compares to alternatives.
Why I Chose Semantic SEO After Google Ads
The keywords I initially targeted through paid search were:
-
human hair wigs
-
glueless wigs
-
lace front wigs
-
blonde wig
-
virgin hair
-
remy hair
I knew these had real buyer intent. But I needed a cost-effective strategy that could compound over time, unlike paid ads that stop the moment you stop paying.
Semantic SEO gave me that edge.
How I Created 1200 Pages Using Semantic SEO
Step 1: Keyword Clustering with Intent
Instead of creating isolated product pages, I built clusters of content using semantic keywords:
-
blonde wigs with dark roots
-
short lace front wigs for summer
-
how to style a virgin hair wig
-
best glueless wigs for alopecia
Each of these supported the main commercial page while answering long-tail queries. This matched user intent and helped me dominate a topic, not just a term.
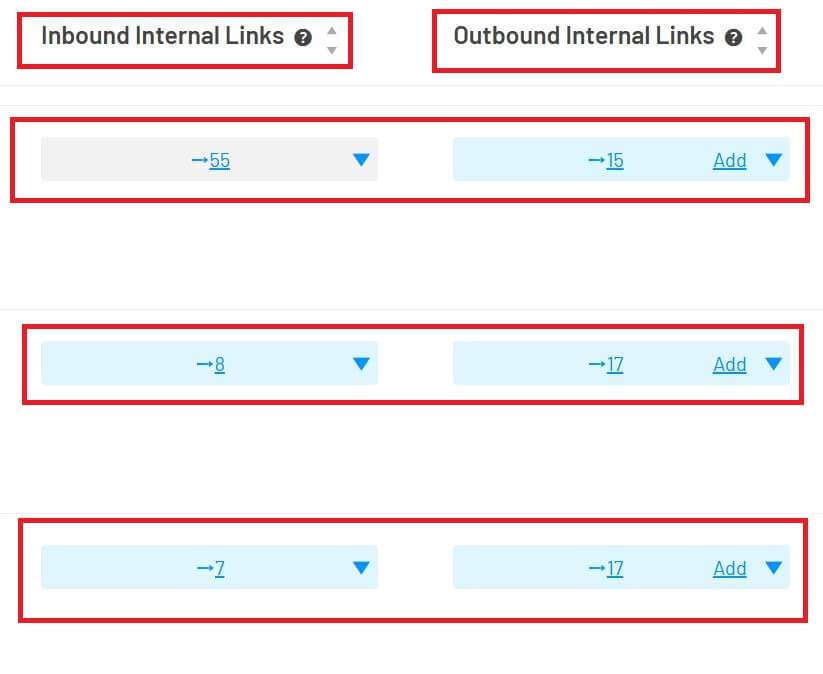
Step 2: Semantic Internal Linking
I built a web of connections across the site:
-
Subpages linked back to their parent “pillar” page
-
Blogs are linked to both product pages and other informational content
-
Tags and category pages acted as hubs
This gave Google a clear semantic map of my site and improved crawlability.
Entity-Based SEO and Semantic Relationships
Google uses “entities” to understand meaning—people, places, products, and more. I used this concept to guide my content creation.
Each page referenced:
-
Product features (e.g., remy hair, cap construction)
-
Use cases (e.g., wigs for cancer patients, cosplay wigs)
-
Styling and care tips (e.g., washing, detangling, storage)
This moved me from just being keyword-focused to being topically authoritative.
Semantic SEO vs Traditional SEO
| Feature | Traditional SEO | Semantic SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Keyword Focus | Exact match | Topic clusters |
| Linking Structure | Flat | Intent-based and structured |
| Google Understanding | Surface-level | Deep contextual relevance |
| Scalability | Manual and isolated | Systematic and scalable |
With traditional SEO, I ranked some pages. With semantic SEO, I ranked full clusters and earned broader visibility.
On-Page Optimization for Semantic Search
Every page I created had:
-
Optimized H1 and H2 with semantic terms
-
Schema markup (product, FAQ, article)
-
Question-answer sections for Featured Snippets
-
Descriptive image alt texts and file names
-
Conversational tone for voice search and AI answers
Featured Snippets, PAA results, and even voice search wins followed.
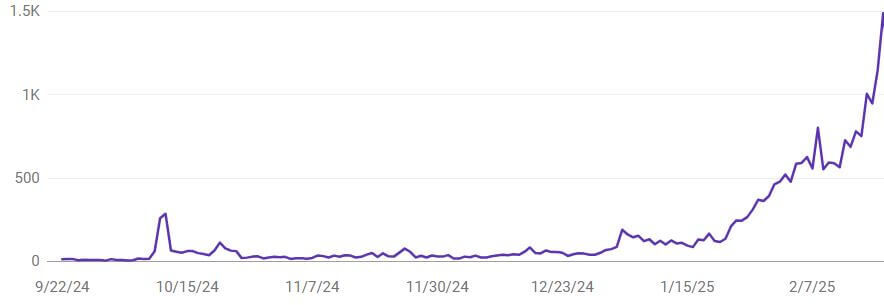
Real-Life Semantic SEO Results
-
1200 pages built with a semantic structure
-
Organic traffic replaced expensive ad clicks
-
Featured snippets and voice search wins
-
Top rankings for multiple keyword clusters
-
Higher time on site, better engagement
Google Search Console showed me clearly—pages that used semantic structure performed consistently better than those that didn’t.
Common Semantic SEO Questions
What is semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is optimizing content so Google understands the meaning, not just the words. It uses topics, entities, and context.
Why did I switch to semantic SEO from paid ads?
Google Ads were unsustainable due to high CPC. Semantic SEO gave me scalable traffic without the recurring cost.
What’s a good example of semantic SEO for e-commerce?
Instead of a single page on “lace front wigs,” create supporting content like “How to style lace front wigs,” “Best lace front wigs for beginners,” and “Synthetic vs. human hair lace wigs.”
How is semantic SEO better than traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO focuses on isolated keywords. Semantic SEO builds trust with Google by covering entire topics with depth and clarity.
Final Thoughts
I started with paid ads and quickly saw that it wasn’t viable long-term. So I pivoted—hard—into Semantic SEO.
By focusing on semantic keywords, entity relationships, and a strategic internal linking structure, I turned my e-commerce website from an expensive ad machine into a sustainable traffic engine.
And you can do the same.
Semantic SEO works. Not in theory, but in practice. Just like it did for me on FrasatAli.com.
Frasat Ali is a seasoned SEO Manager with over a decade of experience helping websites improve visibility through ethical, data-backed strategies. He shares actionable SEO insights grounded in real-world success. Read More
![]()

